Zhang Jinxia
Shougang Hospital of Beijing University, China
Title: Potential antigen targets profiling for colorectal cancer immunotherapy
Biography
Biography: Zhang Jinxia
Abstract
Background: Adoptive chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells and immune checkpoint inhibitors have been proven to be the promising therapies for the treatment of solid tumors in recent years. However, the cell surface antigen expression plays a vital role in both of these immunotherapies. In this study, we investigated the expression of 6 cancer-associated antigens( epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM); carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA); epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR); mesothelin;mucin 1(MUC1); epidermal growth factor receptor 2(HER2)) and 4 immune microenvironments associated markers(CD3 ; programmed death 1(PD1); programmed death-ligand 1 ( PDL1) ; forkhead box P3(FOXP3))in colorectal cancer.
Methods: All available formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor slides from 113 colorectal patients were reviewed. Intensity and distribution for each antigen were assessed by immunohistochemistry.
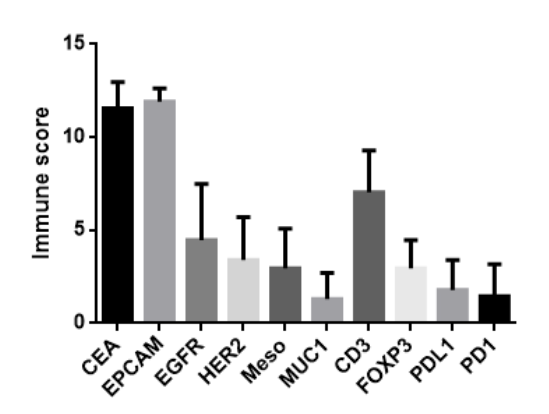
Results: Positive expression of EpCAM, CEA, EGFR, Mesothelin, MUC1, and HER2 were demonstrated in100%, 99%, 96%, 68%, 67% and 37% of colorectal cancer respectively. As for immune microenvironment, CD3, PD1, PDL1 and FOXP3 were positive in 100%, 73%, 71%,97% colorectal cancer cases. More than 90% cases had≧75% distribution of EpCAM-positive cells and CEA-positive cells. More than 50% cases had≧50% distribution of CD3-positive cells, in which almost 40% CD3 positive cells were also FOXP3 positive. However, the PD1 and PDL1 expression were very low in colorectal cancer.
Conclusion: EpCAM and CEA expression were very high in colorectal cancer, which could be the potentially promising targets for colorectal cancer CAR T cell therapy. Although PD1 and PDL1 expression were low in colorectal cancer microenvironment, it could be another strategy by targeting regulatory T cells (FOXP3 positive) to relieve the immunosuppression and enhance the antitumor function of the immune system for colorectal cancer patients.
Figure1. The expression of 6 cancer-associated antigens and 4 immune microenvironment associated markers in colorectal cancer.
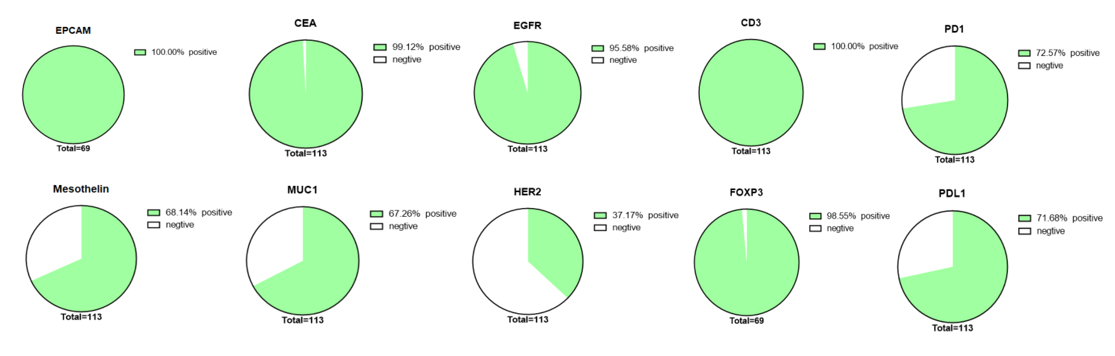
Figure2. The immune scores of 6 cancer-associated antigens and 4 immune microenvironment associated markers in colorectal cancer.